Bridge Wind-Tunnel Analysis
We 3D printed the Golden Gate Bridge, Bay Bridge, and Sydney Harbour Bridge and tested for the aerodynamic performance in the UC Berkeley Wind Tunnel.
What We Did:
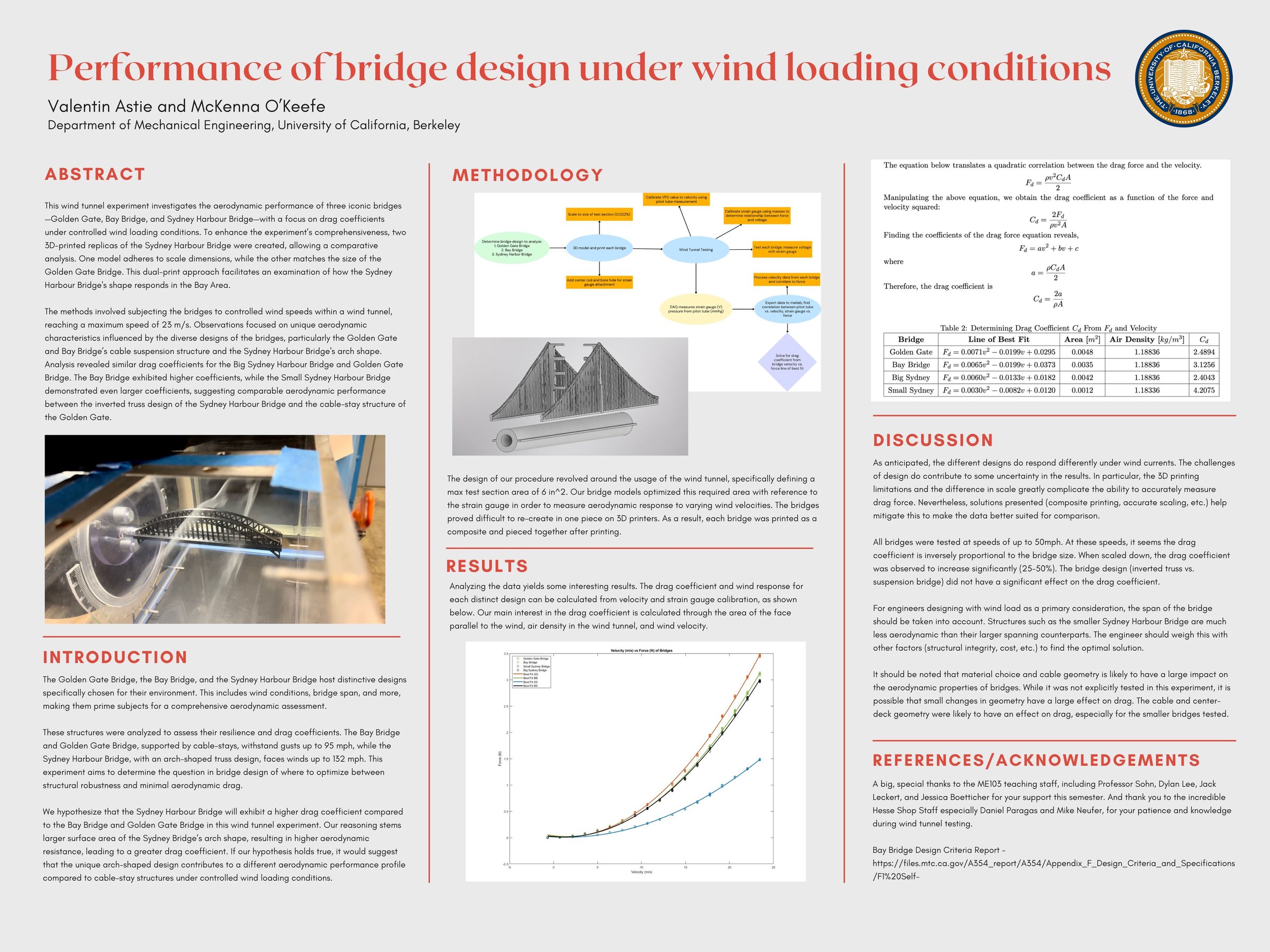
This wind tunnel experiment aimed to assess the how the shape and design of three iconic bridges (Golden Gate, Bay Bridge, and Sydney Harbour Bridge) perform under various wind conditions.
Analysis revealed that bridge span plays a crucial role in determining aerodynamic characteristics, with smaller bridges exhibiting higher drag coefficients. Contrary to initial hypotheses, the experiment emphasized that the span, rather than the specific geometry, significantly influences the aerodynamic performance of bridges under wind loading conditions.
Skills:
CAD
Fusion360
Solidworks
FEA Analysis
3D Printing
Data Analysis
Matlab
Wind-tunnel usage and sensor calibration
Error propogation and analysis
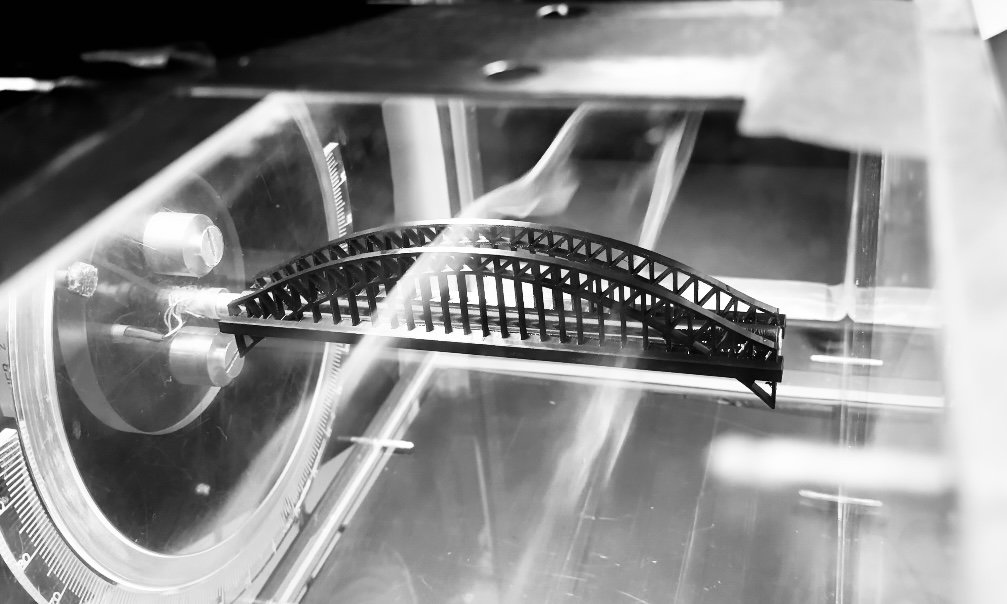

Flow visualization of Sydney Harbour Bridge

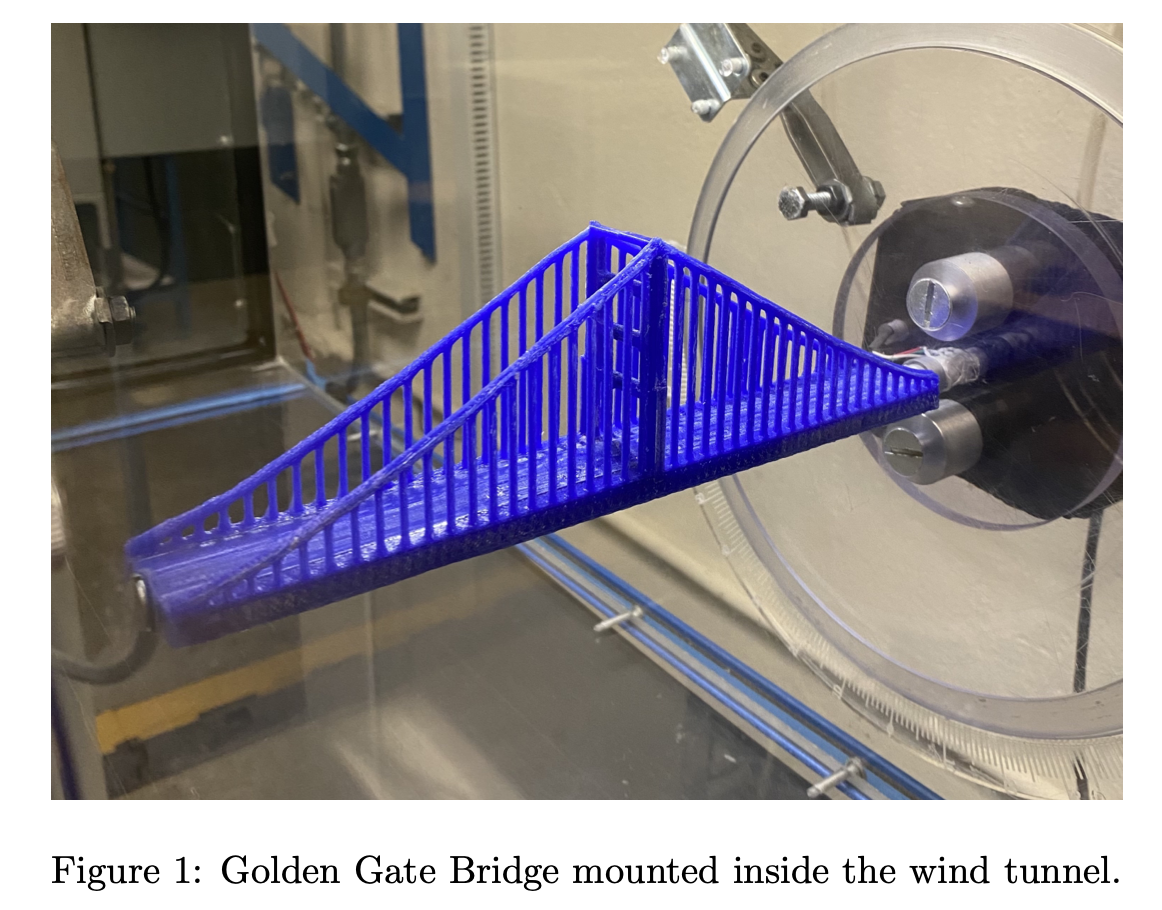
Golden Gate and Bay Bridge printed to scale
Calibrating strain gauge in wind tunnel
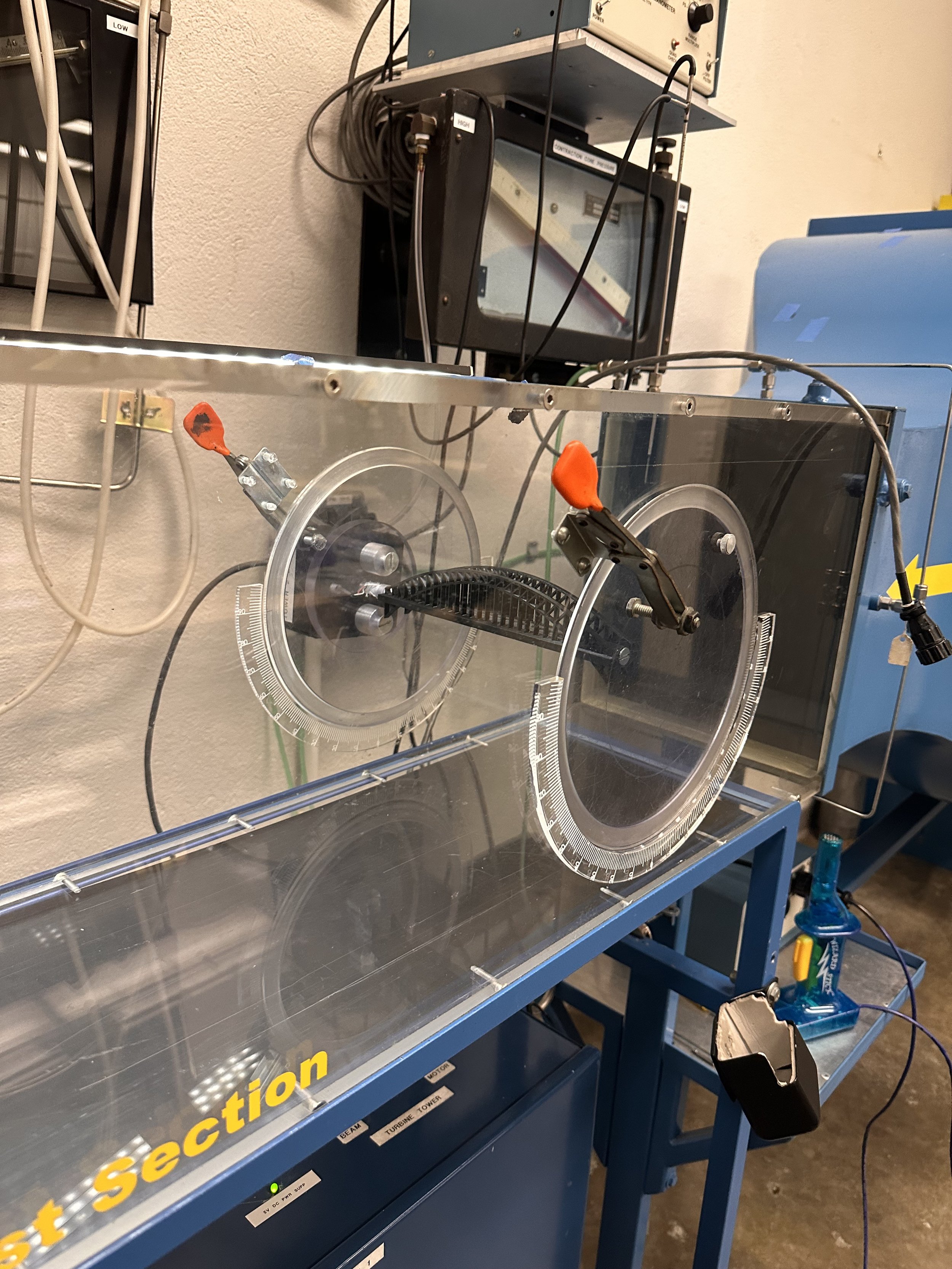

Sydney Harbour Bridge mounted in wind tunnel
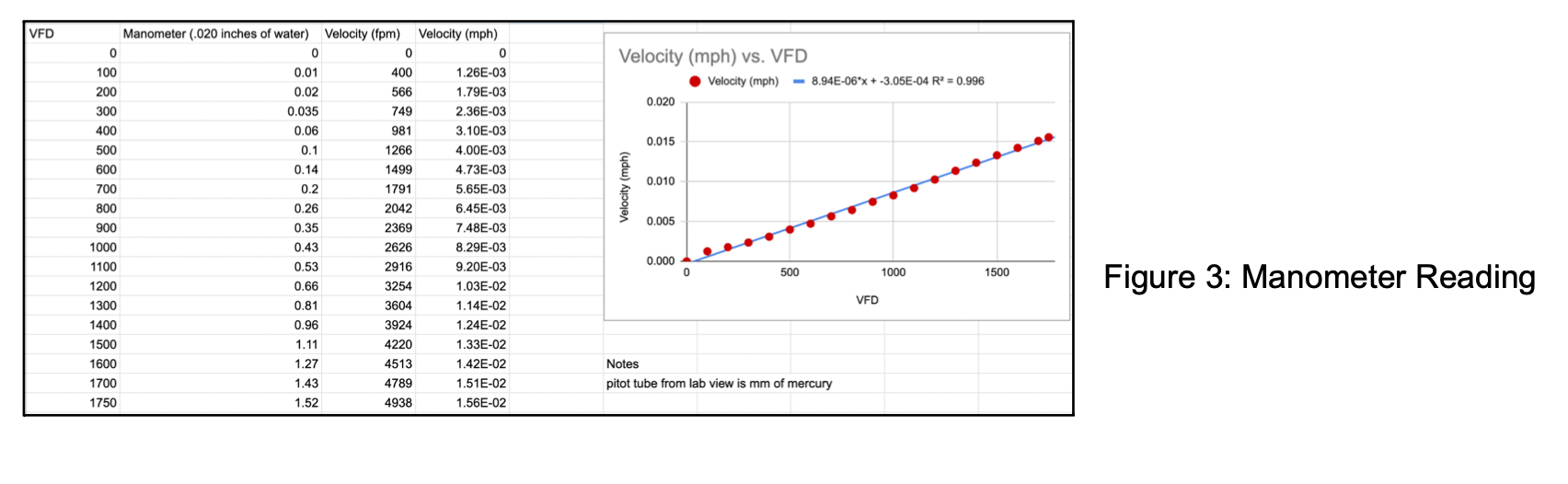
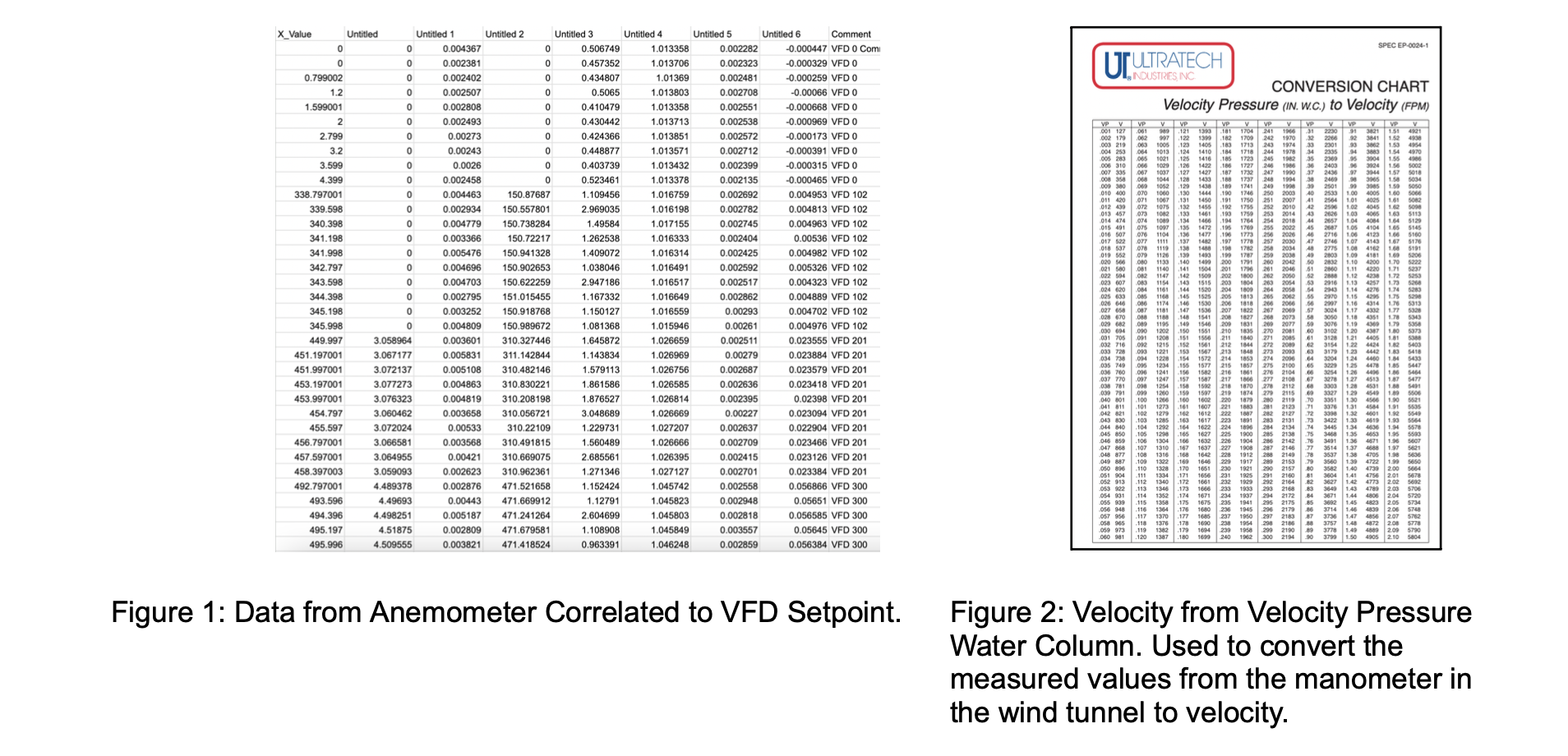
Calibrating manometer reading from inside wind tunnel with VFD, to correlate VFD with velocity

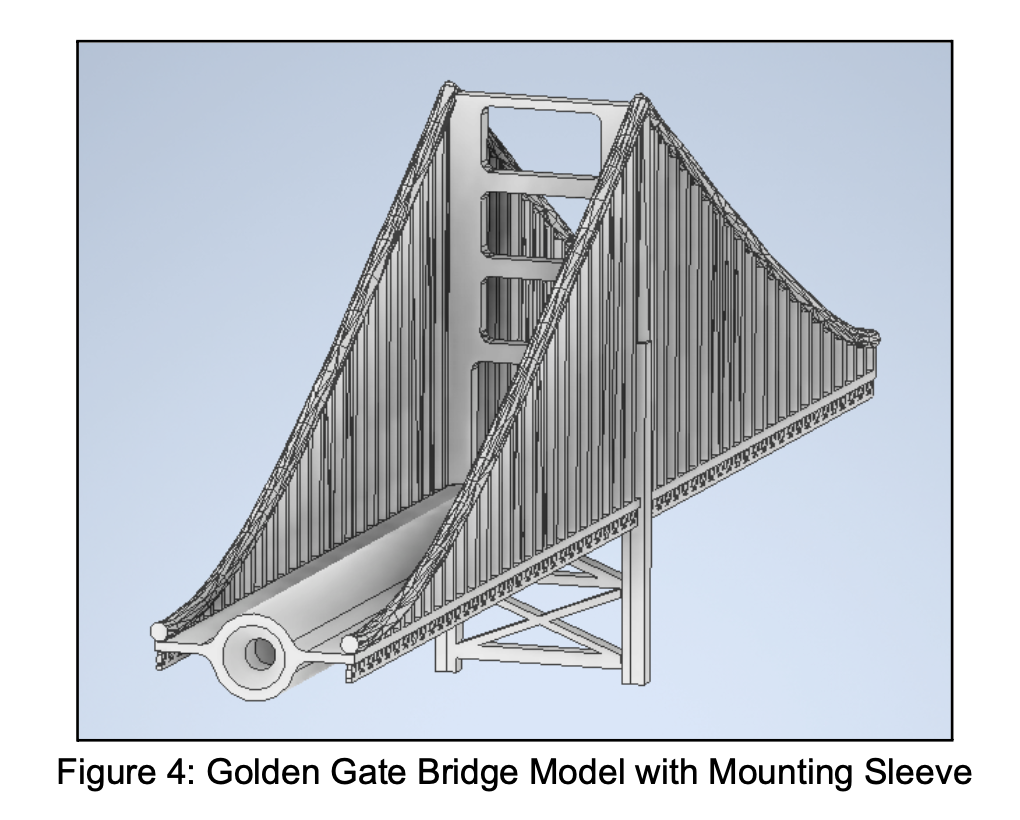
CAD of Golden Gate. Counter-sunk bore hole allows wind tunnel mounting rod to slide inside tube without contact until bolt. This ensures the net force acts on only one point on the rod, resulting in more accurate measurements from the strain gauge.
Printing Golden Gate
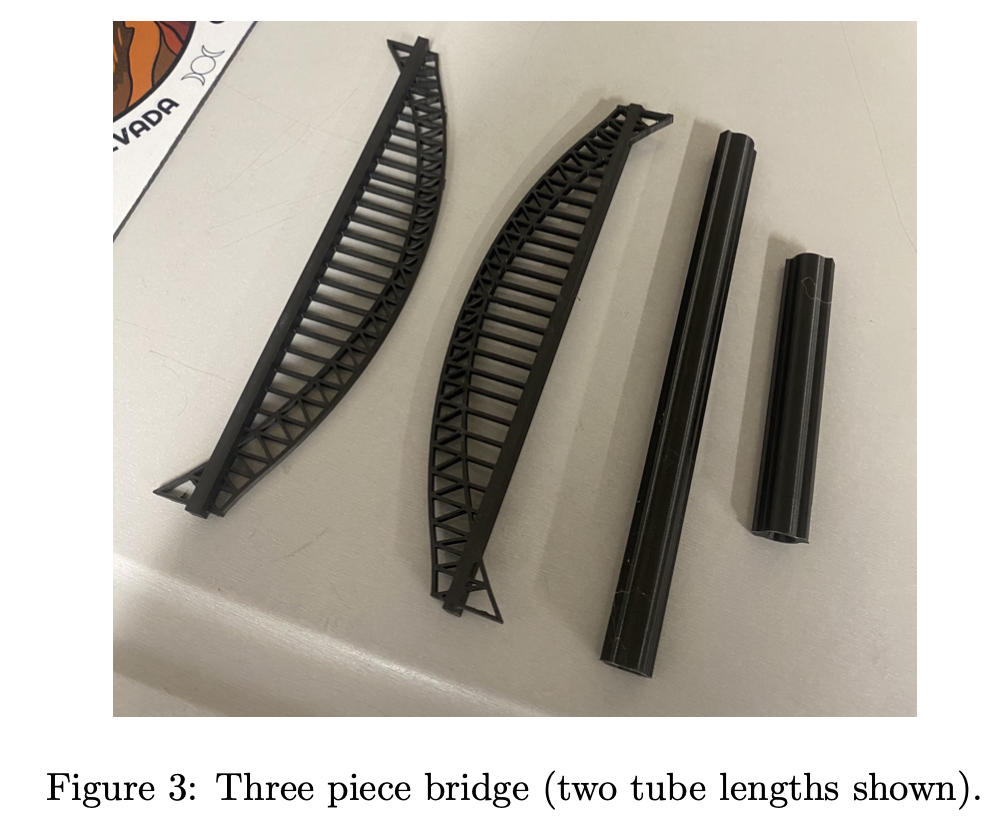

DFM - given the size of the 3D printer bed, needed to break up the birdges and mounting rod into segments to ensure strength.

Finished poster!